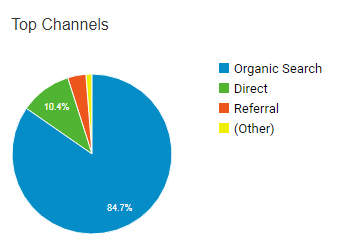
This is the stage where, once the website is actually built, it’ll be launched into cyberspace, with all the stuff that can only be added at the end such as the security certificate, analytics and search engine monitoring tools.
Based in Ilkeston, Derbyshire, and serving the Nottingham and Derby area, I provide website services, including development, for small to medium businesses.
1. Copy Website to Live Server
The website would have been built offline so that it is not publicly accessible until finished.
Think of it as a ship being built in a shipyard, before being launched into the ocean.
You will of course been privy to all progress since I would have been sending you videos and private test versions of the website.
At this stage, the site will not show up in search engines – not until the URL is submitted to each search engine.
Once the URL has been submitted to each engine, the website will be eligible to show up in search results.
2. Install Security Certificate (https)
The security certificate (known as SSL or TLS) will be installed once the website is live.
If it is not installed correctly, you’ll see something like this:
It’s important that all links and media use https in order to have the green padlock show, like this:
In the planning section, I talked about using Dreamhost as your web host, as they include https for free because they’re partnered with Let’s Encrypt.
3. Install Google Analytics 4
Google provides a suite of tools for measuring website traffic, which I can install for you. It can be configured to a basic level for basic tracking or more advanced measurements can be added.
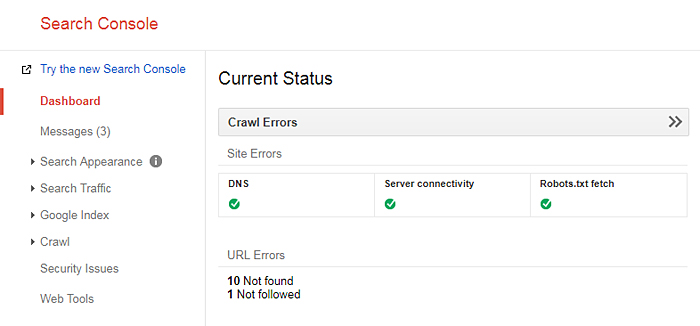
4. Add Site to Google Search Console
Google Search Console is free and will monitor the health of your site. If there are problems, it’ll let you know with suggestions on corrective action.
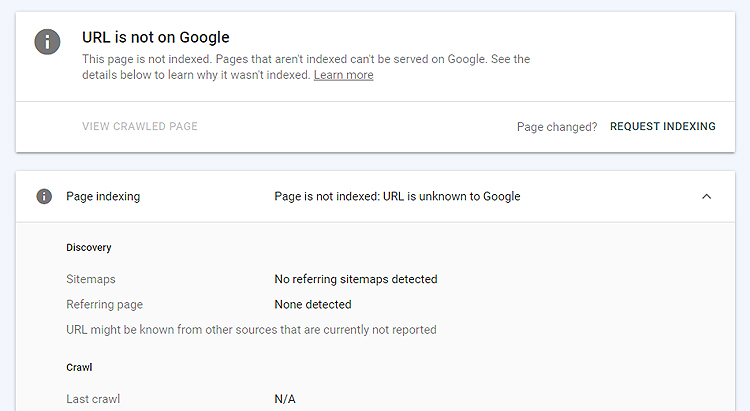
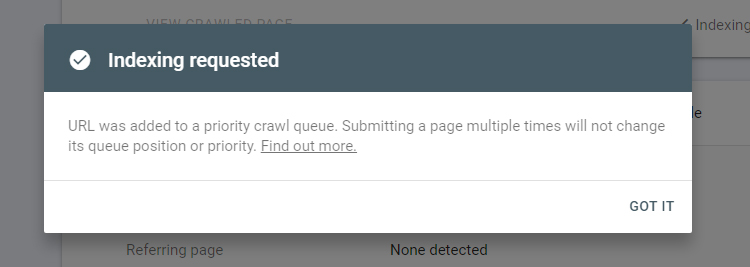
This tool also has the ability (among other things) to request that certain pages be considered for inclusion Google’s index, but with no guarantee that it will actually happen.
Please note that indexing is not the same as ranking. Your site can still be indexed but may not be ranking well (usually because of heavy existing competition).
5. Restrict Certain Pages from Search Engines
Some pages will be deliberately hidden from search engines, as we wouldn’t want every page of the site to show up in search engine results.
If you’ve got landing pages for a Google Adwords ads, these might be deindexed from search results and only ever be accessed by a visitor when they click a specific ad.
There might also be password-protected pages that only staff or VIP customers would ever need to access, which would also need to be hidden from search engines.
New Website Guide
Menu
- ⚖️ Quote Submission
- 🗃️ Preparation
- ♟️ Planning
- 📰 Layout
- 🖇️ Content Preparation
- 🧩 Content Integration
- 📐 Design
- 🪛 Technical and Usability
- ⚙️ Putting It Online